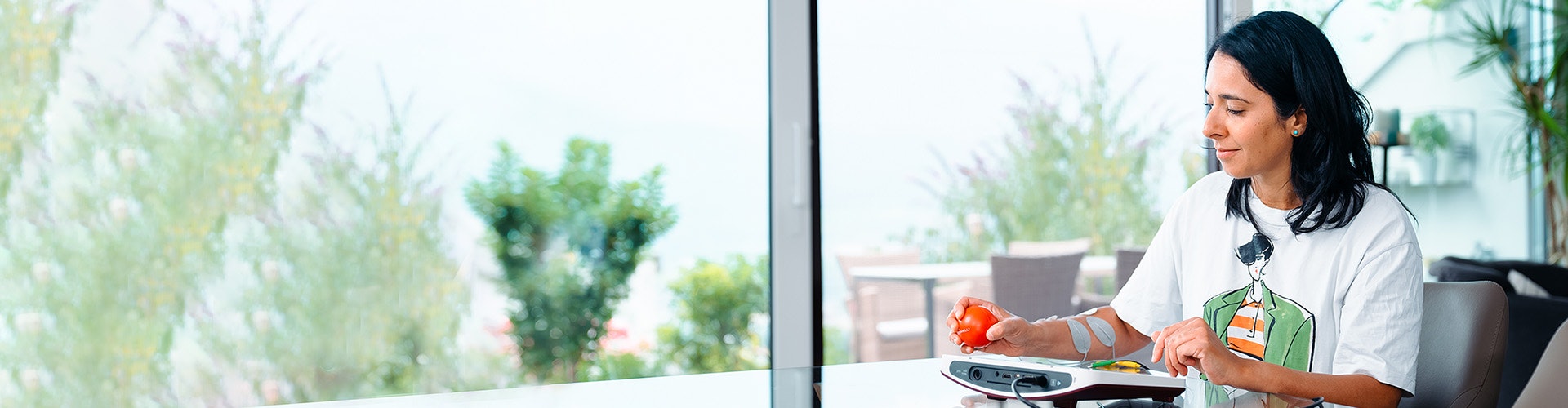
Application Areas
of (functional) electrical stimulation
Functional electrical stimulation (FES)
for orthopaedics & traumatology
-for-orthopaedics-traumatology.png?auto=format&sfvrsn=987db942_28)
FES is used for training movements and for muscle strengthening in rehabilitation after accidents & surgery (e.g. shoulder, hand, hip, knee), and in the treatment of orthopaedic diseases, such as herniated disc, osteoarthritis, and muscle weakness.
Therapy goals
- Re-learning physiological motion sequences
- Improvement of the sense of movement after immobilisation
- Functional improvement
- Increase in muscle strength, endurance, and selective muscle activity, and improvement of coordination
- Improved muscle relaxation
- Reduction of swelling and pain
- Improvement of circulation
- Improvement of connective tissue and joint mobility
- Improved independence & quality of life
Areas of application
Patients with:
- herniated disc (protrusion/prolapse)
- muscle weakness after injuries, immobilisation, or implantation of joint endoprostheses (e.g. knee, hip, shoulder joint)
- unstable joints
- polytrauma
- post-traumatic swelling
- acute and chronic pain
- tendon and muscle transposition
- amputations and replantations
- rheumatoid arthritis

Muscle strengthening
(EMG)

Status post
knee injury
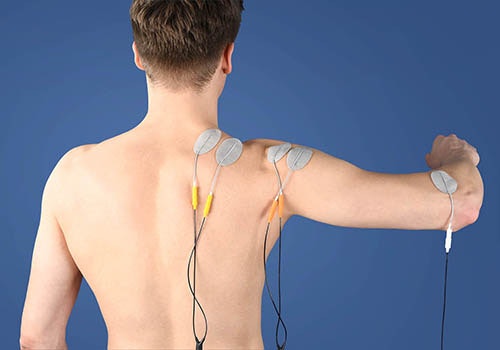
Lift arm without compensation (EMG)
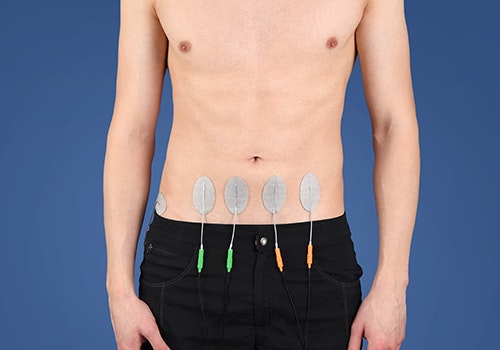
Medium-frequency
(EMG)
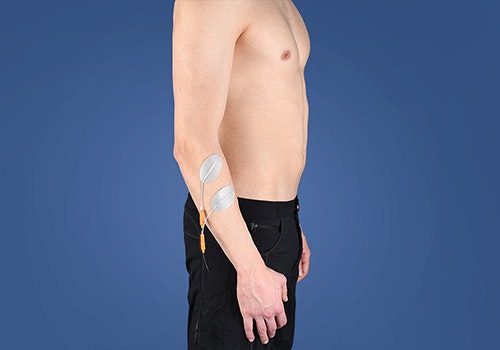
Circulation
improvement
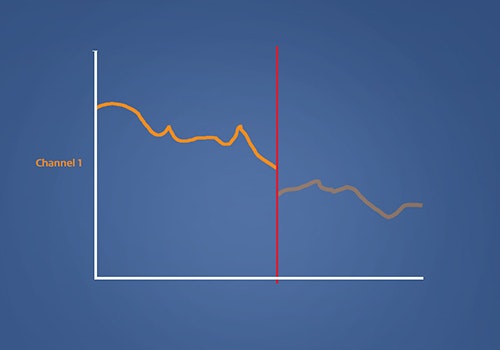
Analysis of muscle activity (EMG)
Muscle strengthening and support for the training of everyday movements
EMG-triggered multi-channel electrical stimulation with the STIWELL® electrical stimulation device enables the stimulation of up to four different muscle groups in the correct sequence. The patient triggers the stimulation on his own using the EMG trigger. This strengthens the muscle activity that was weakened due to injury or surgery.
Studies demonstrate that the additional electrotherapy facilitates an increase in muscle strength (Mistry et al. 2016), and improves quality of life as compared to physiotherapy alone (Avramidis et al. 2011). FES is a good alternative for patients with rheumatoid arthritis who cannot strengthen their muscles by means of resistance training due to their disease (Piva et al. 2018).
Added benefits of therapy with STIWELL®
The treatment of orthopaedic and traumatological conditions often focuses on therapy involving compensatory movements. EMG-triggered STIWELL® programmes can be used specifically for this purpose. In addition, the visual biofeedback function facilitates coordinative muscle strengthening and provides relaxation training. The comprehensive therapy includes treatment options to reduce swelling and pain using low-frequency and medium-frequency currents.
STIWELL® user stories

Nelly
"The device helped me in the rehabilitation of my leg muscles, which were weakened by knee surgery... I am grateful that I had the opportunity to use the STIWELL®, and I would like to recommend it to other patients who have problems with muscle weakness."
Avramidis, K., Karachalios, T., Popotonasios, K., Sacorafas, D., Papathanasiades, A. A., & Malizos, K. N. (2011). Does electric stimulation of the vastus medialis muscle influence rehabilitation after total knee replacement?. Orthopedics, 34(3), 175.
Mistry, J. B., Elmallah, R. D., Bhave, A., Chughtai, M., Cherian, J. J., McGinn, T., Harwin S. F. & Mont, M. A. (2016). Rehabilitative guidelines after total knee arthroplasty: a review. The journal of knee surgery, 29(03), 201-217.
Piva
SR, Khoja SS, Toledo FGS, Wasko MC, Fitzgerald GK, Goodpaster BH, Smith
CN,
Delitto A. Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation Compared to Volitional
Exercise
in Improving Muscle Function in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Randomized Pilot
Study.
Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2018 May 21.
