Application Areas
of (functional) electrical stimulation
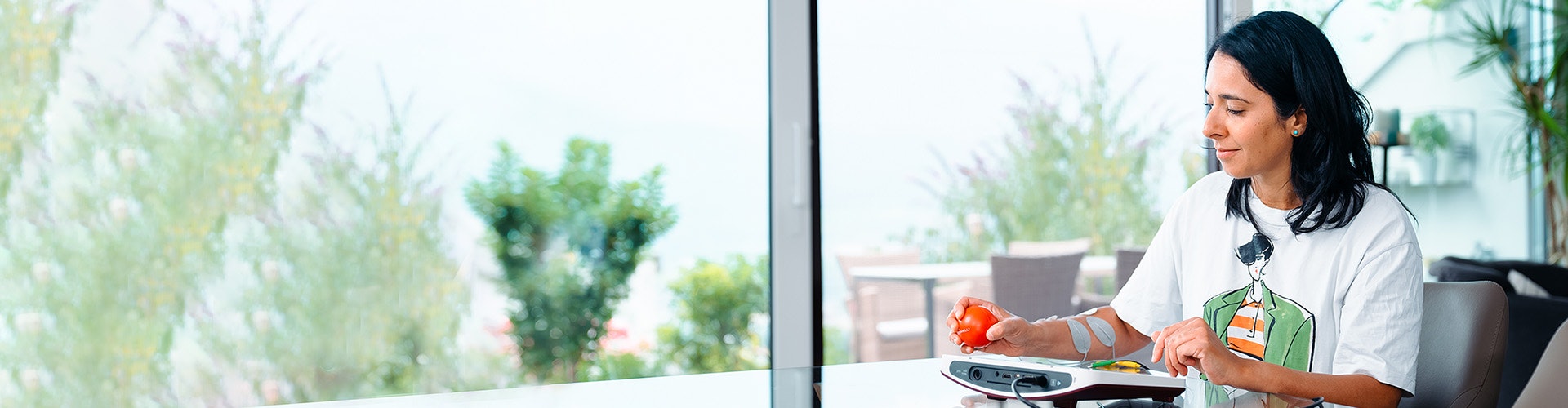
Functional electrical stimulation (FES) for hand injury
-for-hand-injury.png?auto=format&sfvrsn=ee7cb942_22)
The STIWELL® offers a wide range of therapeutic options for arm and hand rehabilitation (for injuries, surgeries, chronic complaints) from the acute to the chronic phase. It can also have a positive impact on a wide diversity of accompanying symptoms.
Therapy goals
- Re-learning of physiological movements and the grasping function
- Restoration of joint function (mobility/stability)
- Improvement of strength, endurance, and coordination
- Improved viscoelasticity of connective tissue
- Functional recovery of peripheral nerve damage capable of regeneration (lower motor neuron)
- Promotion of nerve regeneration (reinnervation)
- Improvement of circulation
- Reduction of swelling and pain
Areas of application
Patients with:
- injuries to bones, muscles, tendons, joint capsules, ligaments, and nerves
- nerve lesions and nerve compression syndrome
- muscle weakness (atrophy) after immobilisation/injury
- overload syndromes: Tendinopathy, etc.
- post-traumatic swelling
- acute and chronic pain
- complex regional pain syndrome (CRPS)
- tendon and muscle transposition
- amputations and replantations
- rheumatoid arthritis
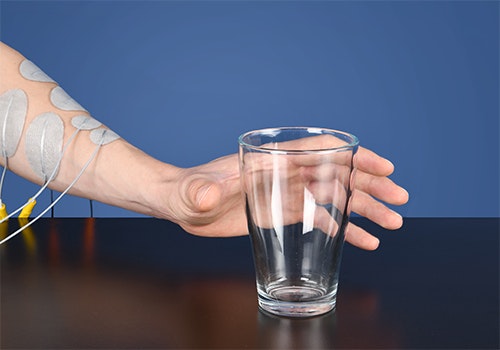
Grasp and release unilateral (EMG)
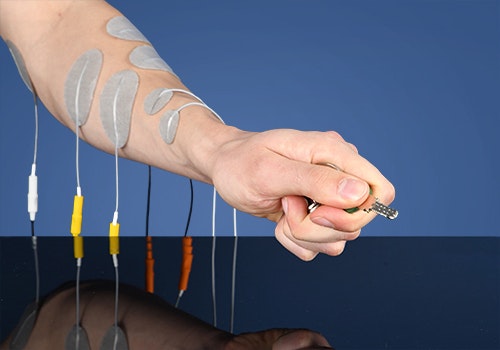
Key grip
(EMG)
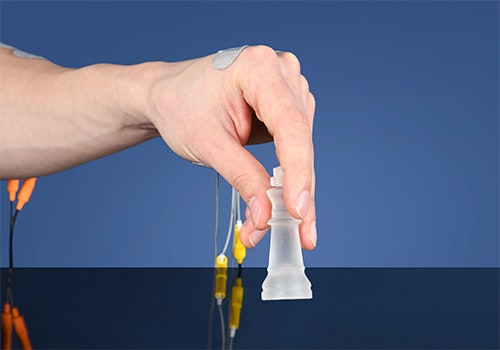
Tripod grasp
(EMG)
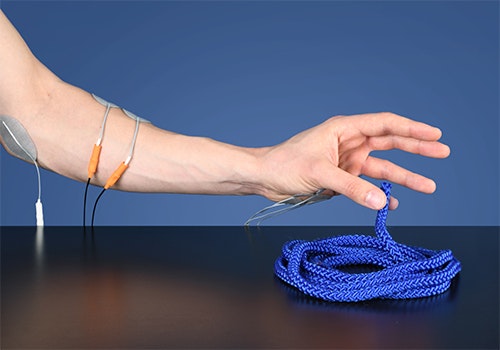
Finger opposition
(EMG)
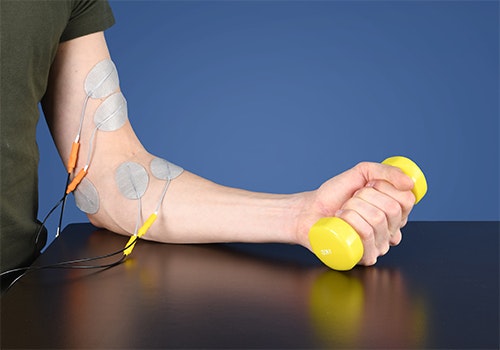
Pronation and supination (EMG)

Spherical grasp
(EMG)
Nerve regeneration, muscle strengthening, and support for the training of everyday movements
FES is applied mainly in the active training phase to restore the joint and gripping function. Everyday movements can be improved by multi-channel stimulation and the option of EMG-triggered movement (Hara et al. 2013). Functional training can also increase strength, and improve endurance and coordination. It is also possible to train with just the STIWELL® biofeedback programmes and purely visual feedback.
In the treatment of lesions of the lower motor neuron in (partial) denervation, the STIWELL® is used to improve the function, mobility, blood circulation, and reinnervation (Gordon & English 2016).
Added benefits of therapy with the STIWELL®
The STIWELL® also has a positive impact on a wide variety of symptoms accompanying arm and hand injuries. Swelling, connective tissue adhesions, or pain can be treated within functional training or through custom programmes.
STIWELL® user stories

Theo used the STIWELL® for nerve regeneration after his two hands were transplanted.
"It has been a huge success. Thanks to the STIWELL®, I can use my new hands completely."
Gordon, T., & English, A. W. (2016). Strategies to promote peripheral nerve regeneration: electrical stimulation and/or exercise. European Journal of Neuroscience, 43(3), 336-350.
Hara, Y., Obayashi, S., Tsujiuchi, K., & Muraoka, Y. (2013). The effects of electromyography‑controlled functional electrical stimulation on upper extremity function and cortical perfusion in stroke patients. Clinical Neurophysiology, 124(10), 2008‑2015.
